
The recognition of depreciation causes a reduction to the pre-tax income (or earnings before taxes, “EBT”) for each period, thereby effectively creating a tax benefit. Under U.S. GAAP, depreciation reduces the book value of a company’s property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) over its estimated useful life. Common expenses that are deductible include depreciation, amortization, mortgage payments, and interest expense. There are cases where income can be lowered for a certain year due to previously unclaimed tax losses from prior years. The booked Depreciation Tax shield is under the Straight Line method as per the company act.
- This method is not only straightforward but also aligns with the matching principle in accounting, which stipulates that expenses should be matched with the revenues they help to generate.
- With over 20 years of experience, TaxShield and our Chartered Quantity Surveyors have completed tens of thousands of reports.
- Tax shield for an individual is beneficial when you want to buy a home, using a mortgage or a loan.
- As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
The 2007 Financial Crisis: A Deep Dive into the Bonguest Theory
- The cost allocation in the form of depreciation will ultimately ensure that the final value of the asset appearing in the financial statement will reflect its true and fair current value.
- The most significant advantage of debt over equity is that debt capital carries significant tax advantages as compared to equity capital.
- This process, known as a tax shield, serves as a legal method to defer taxes, improving cash flow and potentially enhancing the value of the business.
- However, it is important to consider the effect of temporary differences between depreciation and capital cost allowance for tax purposes.
- These are the tax benefits derived from the creative structuring of a financial arrangement.
In the realm of business strategy, the anticipation of regulatory changes plays a pivotal role in… For example, the child tax credit deducts up to $2,000 per dependent age sixteen or younger. In addition, bookkeeping paying for childcare can net you $3,000 for one dependent twelve or younger and $6,000 for two or more dependents.
The Tax Shield Theory in Corporate Finance: A Comprehensive Guide
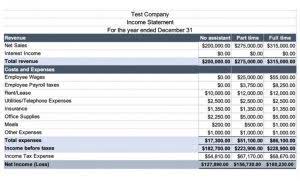
Companies must carefully balance the advantages of debt with the potential costs of bankruptcy. Partnered with Chartered Quantity Surveyors who are experts in tax depreciation, we are dedicated to helping property investors and business owners reach their financial goals. Our passion for saving you money supports reinvestment in housing and businesses, boosting the economy. Because depreciation expense is treated as a non-cash add-back, it is added back to net income on the cash flow statement (CFS). In the final step, the depreciation expense — typically an estimated amount based on historical spending (i.e. a percentage of Capex) and management guidance — is multiplied by the tax rate. The use of a depreciation tax shield is most applicable in asset-intensive industries, where there are https://jacoblessons.com/guide-to-predetermined-overhead-rate-formula-2/ large amounts of fixed assets that can be depreciated.
Business Expenses

It effectively lowers the net cost of acquiring new assets, making investments in property, plant, and equipment more financially attractive. By understanding and leveraging this tax benefit, businesses can optimize their tax liabilities and allocate resources more effectively for growth and operational needs. From the perspective of a small business owner, the straight-line depreciation method offers simplicity and predictability, allowing for a uniform tax shield year after year. For instance, consider a business that purchases a piece of equipment for $100,000 with a useful life of 10 years. Using straight-line depreciation, the business can deduct $10,000 each tax shield depreciation year, providing a consistent annual tax saving that can be factored into cash flow projections. For instance, when a company acquires an asset, it can deploy the straight-line depreciation method, which allocates the cost of the asset evenly over its useful life.
Unlocking Financial Benefits
This is because the net effect of losing a tax shield is losing the value of the tax shield but gaining back the original expense as income. The intuition here is that the company has an $800,000 reduction in taxable income since the interest expense is deductible. However, when we calculate depreciation tax shield, even though the tax amount is reduced due to depreciation, the company may eventually sell the asset at a profit. The concept of depreciation tax shield deals with the process in which there is a reduction in the tax amount to be paid on the income earned from the business due to depreciation. In the process, the amount of depreciation is used to reduce the income on which tax will be charged, thus bringing down the amount of tax payment.


Conversely, for a stable corporation with predictable profits, the straight-line method could provide a reliable annual tax shield that aids in long-term financial planning. The concept of a tax shield is a fundamental strategy in financial planning, offering both immediate and long-term benefits. At its core, a tax shield serves as a method to reduce taxable income through allowable deductions such as depreciation, mortgage interest, or amortization. This reduction in taxable income translates to immediate savings in the form of lower tax payments. For businesses, this can significantly impact cash flows, allowing for reinvestment or debt servicing.
